The alarming rate of groundwater depletion and unpredictable monsoons have made stp plant systems the most important guardians of our water resources. Water conservation challenges we face today are unprecedented, which makes sewage treatment plant technology crucial now more than ever before.
Underground STP plants are vital to recycling and reusing water. These systems clean and purify wastewater effectively to protect our environment and public health. The sewage plant treatment systems help us conserve water and deliver environmental benefits. To name just one example, wastewater treatment generates much methane gas that we can use for energy production. The treatment residue becomes a source of organic fertilizers. Modern underground STP plant designs produce minimal odors and can serve for up to 15 years or longer with proper maintenance.
This piece will help you understand how stp plant works. You will learn the core benefits of underground systems and everything you need to know about implementing these environmentally responsible water management solutions.
What is an Underground Sewage Treatment Plant?

Underground sewage treatment plants (USTP) are a state-of-the-art advancement in wastewater management technology. These systems work beneath the surface and process wastewater from homes, businesses, and industries. They purify it to meet safety standards for environmental discharge or reuse.
Definition and comparison with traditional STP systems
Underground STPs clean wastewater through physical, biological, and sometimes chemical processes—like conventional systems—but with important structural differences. Traditional sewage treatment plants take up valuable surface space with visible tanks, machinery, and piping that can spoil landscapes. Underground facilities stay hidden beneath parking lots, gardens, or even buildings.
These systems are built differently in several ways:
Space Utilization: Traditional STPs need dedicated areas that can’t be used for anything else. Underground systems let you use the land twice—treating wastewater below while supporting gardens, parking, or recreational facilities above.
Operational Characteristics: Regular plants usually employ high-load motors (approximately 20 HP) and blowers that need lots of electrical power. Many underground systems like SUSBIO ECOTREAT use gravity-fed processes, which cuts down energy use.
Maintenance Requirements: Above-ground systems need frequent access to adjust operations and add chemicals. Modern underground designs have well-placed maintenance hatches and inspection ports that make servicing easy without major digging.
Environmental Protection: The underground location naturally insulates against extreme weather. This reduces system failure risks and contains treatment processes better.
Why underground STPs are gaining popularity in urban areas
Underground sewage treatment plants are becoming popular because they solve many modern urban challenges.
These systems help save land—a crucial factor in crowded cities where space is expensive. They work well for dense residential communities and areas with limited land, especially in places far from central treatment facilities.
The underground setup also tackles both odor and noise problems that usually come with wastewater treatment. Bad smells stay contained underground and don’t affect nearby areas. The earth blocks most operational noise, which keeps nearby residents happy.
Underground installations look better because they hide unsightly infrastructure. Architects, developers, and urban planners love this feature as they try to create attractive environments.
Property values stay strong with underground STPs. Regular sewage plants can scare away buyers or reduce property values because people see them as a nuisance. Making these systems “invisible” helps developments stay marketable and attractive.
Compact, modular designs have made it easier to install these systems underground. Modern systems like SUSBIO ECOTREAT show this progress with flexible, prefabricated parts that fit smoothly below ground, even under gardens or paved areas. These engineered solutions clean wastewater well while making the best use of space—exactly what today’s urban infrastructure needs.
How Underground STP Plant Works: Step-by-Step Process
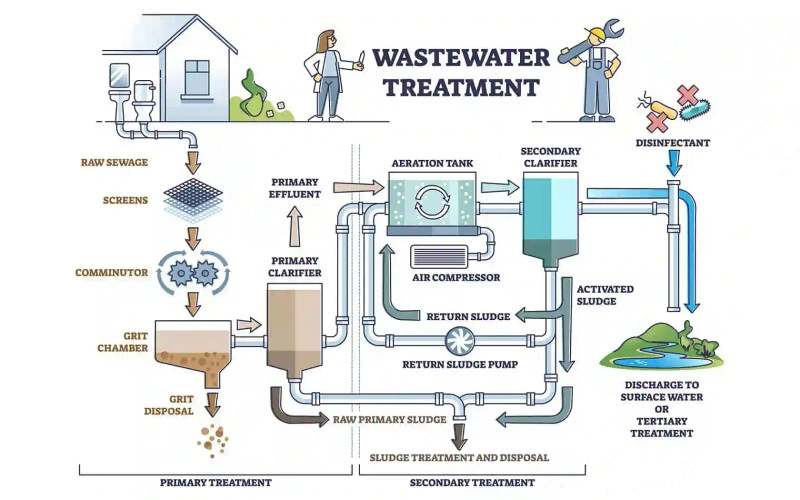
Underground sewage treatment plants clean wastewater through several steps that turn it into reusable water. The treatment happens in stages, and each stage removes specific contaminants.
Primary Treatment: Screening and Sedimentation
The process starts at the screening chamber where screens catch large debris like plastics, rags, and bulky objects. This step protects equipment downstream and keeps the system running smoothly. The wastewater then moves to a grit chamber. Here, the flow slows down so heavy materials like sand, coffee grounds, and eggshells can sink.
Next, the sewage flows into primary sedimentation tanks or clarifiers and stays there for 1.5 to 2.5 hours. Gravity does the work here – heavy solids sink to form primary sludge while oil, grease, and lighter materials float to the top for skimming. This process removes 50-70% of suspended solids and cuts biological oxygen demand (BOD) by 25-40%.
Secondary Treatment: Aeration and Activated Sludge
The next step is biological treatment, which is the core of sewage processing. Underground plants often use activated sludge processes or Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors (MBBR), like those in SUSBIO ECOTREAT systems.
An activated sludge system has an aeration tank and a secondary clarifier. Air pumps through porous diffusers at the bottom of the tank. This adds oxygen and mixes everything thoroughly. Helpful microorganisms grow well in this oxygen-rich environment and eat the dissolved organic matter.
The microbes need about six hours in the aeration tank to reduce the organic load. The mixture then flows to secondary clarifiers where the activated sludge sinks. About 30% of this sludge goes back to the aeration tank to keep the right amount of microbes.
Tertiary Treatment: Filtration and Disinfection
Underground STPs use advanced tertiary processes to get better water quality. This stage removes tough contaminants, nutrients, and harmful organisms.
The treatment includes:
- Filtration using sand, activated carbon, or zeolite to catch remaining solids
- Membrane technology with various filtration methods based on needed water quality
- Nutrient removal to get rid of nitrogen and phosphorus that could harm water bodies
The final step is disinfection, which kills harmful microorganisms before the water leaves the plant. Plants use ultraviolet (UV) light, chlorine, or ozone. Good tertiary treatment can remove 80-90% of phosphorus and COD, and 30-60% of nitrogen.
Sludge Handling and Disposal in Underground Systems
Sludge management plays a vital role in underground STPs. The process starts with thickening, which cuts the sludge volume in half. The thick sludge then goes through digestion – either with or without oxygen – to break down organic solids.
Many underground systems use two-stage anaerobic digestion. First-stage bacteria break big molecules into smaller ones. These smaller molecules then turn into biogas – a mix of methane and carbon dioxide. The plant can use this methane for heat or power.
After digestion, the sludge needs dewatering to remove moisture. Modern underground STPs often use machines like centrifuges or belt filter presses instead of drying beds. These machines give better control and take up less space.
SUSBIO ECOTREAT shows how good sludge management works in underground systems. Its approach creates less sludge and makes disposal easy. This complete system treats wastewater below ground while keeping the space above free for other uses.
Key Components of an Underground STP Plant
Underground STP plants work best when their carefully designed components work together to treat wastewater. These specialized elements are the foundations of modern sewage treatment systems that ensure peak performance in tight spaces.
Bar Screens and Grit Chambers
Bar screens stand as the first defense at every underground sewage treatment plant’s entry point. These screens filter out large debris like sticks, rags, and plastic materials that could damage equipment or block the system. The screens come in two types – coarse screens (6-25mm openings) and fine screens (1-6mm openings) to protect the system’s mechanical parts.
Next, grit chambers reduce wastewater flow speed so heavier particles like sand, gravel, and coffee grounds can settle. This prevents pumps from getting damaged by abrasion and reduces equipment wear. Modern underground STPs use aerated or vortex-type grit chambers that separate heavy inorganic materials while keeping organic matter floating.
Pre-aeration and Primary Settling Tanks
Pre-aeration tanks add air to wastewater before primary treatment to reduce septicity. This releases gasses, cuts down odors, and helps solids settle better.
Primary settling tanks (clarifiers) slow down water flow substantially. This allows suspended solids to sink as primary sludge while oils and grease float up for removal. These tanks remove 60-90% of suspended solids with chemicals and 40-70% without them. Mechanical scrapers move collected sludge to a hopper for processing.
Aeration Tanks and Secondary Clarifiers
The biological treatment phase uses aeration tanks with bottom diffusers to create oxygen-rich environments where good bacteria thrive. These bacteria eat organic pollutants and turn them into carbon dioxide, water, and new bacterial cells. In fact, aeration tanks are the core of the activated sludge process – maybe the most accessible treatment method worldwide.
Secondary clarifiers then separate biological floc (activated sludge) from treated water. Microbial biomass sinks while clean water rises. Some settled sludge goes back to the aeration tank to keep bacterial populations at the right levels, which keeps biological treatment going.
Biological Filters and Sludge Handlers
Biological filters create surfaces where microorganisms stick and digest remaining pollutants. These fixed-film processes need nowhere near as much space as activated sludge systems – just 20-30% of the area. They work great for keeping biomass in place, modular building, and treating diluted wastewater.
Sludge handlers take care of collecting, thickening, and dewatering leftover solids. This equipment gets sludge ready for disposal or reuse through composting or biogas production. Modern underground STPs prefer mechanical systems like centrifuges over traditional drying beds to save space.
Top 5 Benefits of Underground Sewage Treatment Plants
Modern cities are turning to underground sewage treatment solutions more frequently due to their many advantages. These systems provide benefits that go way beyond the reach and influence of basic wastewater processing.
Space Optimization in Urban Infrastructure
Underground STP plants excel at maximizing land use in crowded urban areas. Moving treatment facilities below ground creates valuable space for parking lots, parks, gardens, or new buildings. Property values stay protected – this is a vital point since above-ground sewage treatment plants can reduce surrounding housing prices by up to INR 32.5 billion. Underground installations let cities use land for two purposes at once. They keep the area looking good while handling essential waste processing.
Odor and Noise Reduction for Residential Areas
H₂S emissions create odor problems in regular sewage treatment plants, mostly from inlet pump houses, grilles, and aeration grit tanks. Underground STP plants naturally contain unpleasant smells because earth acts as a barrier that keeps odors away from living spaces. The surrounding soil also muffles operational sounds from pumps and blowers. This creates a quieter environment that works well for residential neighborhoods, hotels, hospitals, and schools.
Energy Efficiency and Biogas Recovery
Wastewater treatment creates lots of methane gas that we can utilize for energy production. Modern biogas recovery systems can generate up to 137 GWh of annual energy (heat and power) when biogas comes from wastewater and sewage sludge. This renewable energy source can power the treatment facility and send extra energy to the national grid. It has potential to avoid 38,500 tCO₂eq emissions each year.
Fertilizer Production from Treated Sludge
Treated sludge has valuable nutrients like nitrogen, ammonium, potassium, and zinc that boost soil fertility. Using sewage sludge as fertilizer cuts down the need for synthetic fertilizers and preserves non-renewable energy sources. On top of that, it creates standard fertilizer products like struvite (magnesium ammonium phosphate) that give plants accessible nitrogen and phosphorus.
Compliance with Environmental Regulations
Underground STP plants help meet strict discharge standards that environmental authorities set. CPCB regulations require treated water to maintain specific parameters: pH (6.5-8.5), BOD (≤10 mg/L), COD (≤50 mg/L), and suspended solids (≤10 mg/L). These systems often perform better than regulatory requirements through advanced filtration and disinfection modules. This ensures proper compliance with environmental standards while promoting green wastewater management practices.
SUSBIO and SUSBIO ECOTREAT: Best-in-Class Underground STP Solutions
SUSBIO guides the way in innovative wastewater solutions with their flagship product, SUSBIO ECOTREAT—a groundbreaking underground sewage treatment plant built for modern infrastructure needs.
Modular Design and Compact Footprint of SUSBIO
SUSBIO ECOTREAT features a prefabricated, modular design made with high-quality fiber-reinforced plastic (FRP) that delivers exceptional durability. The innovative construction helps install it underground smoothly, even beneath landscaped areas or paved surfaces. Its compact size makes it perfect for urban spaces where room is tight. We designed it as a “plug-and-play” solution, and these units come fully assembled, ready to deploy quickly without much civil work.
Energy-Saving Features in SUSBIO ECOTREAT
The system uses up to 90% less electricity than regular sewage treatment plants. This amazing efficiency comes from its advanced dual-treatment process that combines anaerobic and aerobic methods. On top of that, variable frequency drives (VFDs) adjust aeration based on live load conditions, which cuts out wasted energy. The system’s running costs stay low throughout its lifecycle.
Low Maintenance and Long Lifecycle
SUSBIO ECOTREAT runs on sophisticated automation that needs minimal human involvement. The system needs only monthly checks and twice-yearly desludging. The reliable FRP construction fights corrosion and prevents leaks. Self-cleaning mechanisms keep membranes and pumps clear. The modular parts are easy to replace without stopping the whole system. The company backs it with a 10-year warranty on construction materials.
Case Studies: SUSBIO Installations in India
A residential society in Pune switched their old sewage system with SUSBIO ECOTREAT in just a week. They cut energy use by 40% and got rid of odor complaints. Mall De Goa’s SUSBIO installation improved operations by a lot, needed less maintenance, and let them reuse water for landscaping. At luxury holiday villas in Goa, the prefabricated design meant quick installation without hurting the property’s looks.
Why SUSBIO Ecotreat is Ideal for Residential and Commercial Use
SUSBIO ECOTREAT runs quietly below 50 decibels with no odors at all. The system adapts well to projects from single homes to large commercial complexes. Its advanced IoT integration and live monitoring features mean you’ll spend less time on maintenance. The system meets or beats strict environmental standards for safe water reuse or discharge.
Conclusion
Underground sewage treatment plants have become a vital solution to our growing water conservation challenges. This piece explores how these innovative systems operate beneath the surface and deliver remarkable benefits to urban environments while supporting sustainability goals.
Modern underground STPs process wastewater through sophisticated treatment stages. The process starts with screening and sedimentation, moves to biological processing, and ends with tertiary filtration. This complete approach ensures water purity while taking minimal surface space. The subterranean placement naturally contains odors and noise, which makes these systems perfect for residential areas and sensitive locations.
Underground STPs offer benefits that go way beyond their looks. Smart space use allows valuable land to serve two purposes – treating wastewater below while supporting gardens, parking, or recreational facilities above. Energy recovery systems capture methane to generate power, which substantially reduces operational costs and environmental effects. The treated sludge becomes nutrient-rich fertilizer, transforming waste into valuable agricultural resources.
SUSBIO ECOTREAT stands out as an excellent underground STP solution with good reason too. Its prefabricated, modular design allows quick installation with minimal disruption and uses up to 90% less electricity than conventional systems. Durable FRP construction combined with advanced automation reduces maintenance needs and extends operational life. Case studies from India show SUSBIO’s success in settings of all types – from residential complexes to commercial developments.
Water shortage concerns continue to grow worldwide. Underground sewage treatment plants will play a vital role in sustainable water management. These systems strike a perfect balance between functionality, efficiency, and environmental care. SUSBIO ECOTREAT shows us the future of wastewater treatment – invisible below ground yet powerful in its effect on conservation and sustainability.
Key Takeaways
Underground sewage treatment plants represent a revolutionary approach to wastewater management, offering space-efficient solutions while delivering superior environmental and economic benefits for modern urban infrastructure.
• Underground STPs maximize land use by operating beneath surfaces, allowing dual-purpose spaces for parks, parking, or buildings above treatment facilities.
• These systems eliminate odor and noise pollution through natural earth barriers, making them ideal for residential areas and sensitive locations.
• Energy efficiency reaches up to 90% savings compared to conventional plants, with biogas recovery capabilities generating renewable power from methane.
• Treated sludge converts into valuable organic fertilizer, reducing synthetic fertilizer dependency while creating sustainable agricultural resources.
• SUSBIO ECOTREAT exemplifies next-generation underground STP technology with modular design, automated operation, and 10-year construction warranty.
The shift toward underground sewage treatment reflects our urgent need for sustainable water management solutions that preserve valuable urban space while meeting strict environmental standards. These systems prove that effective wastewater treatment doesn’t require sacrificing esthetics or consuming excessive energy—instead, they enhance property values while contributing to circular economy principles through resource recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the main advantages of underground sewage treatment plants?
Underground sewage treatment plants offer several benefits, including space optimization in urban areas, significant reduction in odor and noise pollution, energy efficiency through biogas recovery, production of organic fertilizer from treated sludge, and improved compliance with environmental regulations.
Q2. How do underground sewage treatment plants work?
Underground STPs process wastewater through a series of stages, including screening, sedimentation, biological treatment, and tertiary filtration. The system uses both physical and biological processes to remove contaminants, with microorganisms playing a crucial role in breaking down organic matter.
Q3. Are underground STPs more energy-efficient than traditional systems?
Yes, underground STPs can be significantly more energy-efficient. For example, systems like SUSBIO ECOTREAT can consume up to 90% less electricity compared to conventional sewage treatment plants. They also have the potential to recover biogas for energy production.
Q4. Can the treated water from underground STPs be reused?
While the treated water from underground STPs is not typically safe for drinking, it can be safely reused for various non-potable purposes such as landscaping, irrigation, and industrial processes. The water quality meets or exceeds regulatory standards for safe discharge or reuse.
Q5. What makes SUSBIO ECOTREAT a standout underground STP solution?
SUSBIO ECOTREAT distinguishes itself with its modular, prefabricated design for quick installation, high energy efficiency, low maintenance requirements, and long operational lifespan. It also features advanced automation and IoT integration for real-time monitoring, making it suitable for both residential and commercial applications.






