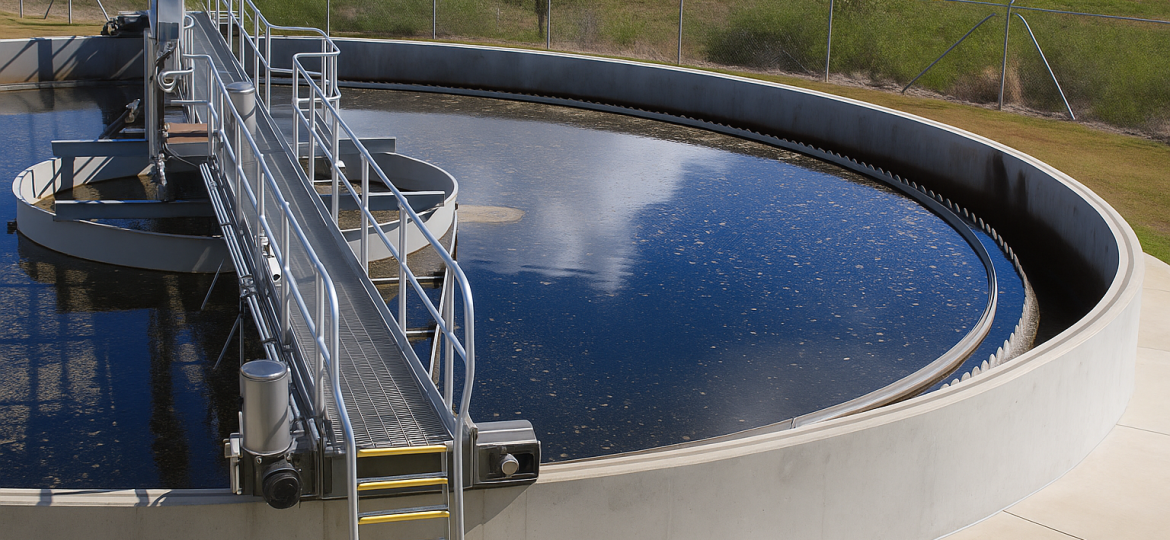
Water is life—but what happens to it after we’ve used it? Every day, billions of liters of wastewater are generated from homes, industries, and commercial establishments. Without proper treatment, this sewage can severely damage the environment, human health, and our water resources. That’s where sewage treatment comes in—a vital process that protects our ecosystems and enables water reuse.
As urban populations grow and water scarcity becomes a pressing issue, advanced sewage treatment technologies are no longer optional—they’re essential. In this blog, we’ll explore the need for sewage treatment, review top technologies in use today, and highlight eco-friendly solutions like SUSBIO ECOTREAT that are paving the way toward a sustainable future.
What Is Sewage Treatment?

Sewage treatment is the process of removing contaminants, organic matter, and pathogens from wastewater before it is released back into the environment or reused. The process typically involves several stages:
- Preliminary Treatment: Removal of large debris and grit.
- Primary Treatment: Settling of solids and separation of sludge.
- Secondary Treatment: Biological breakdown of organic matter using microbes.
- Tertiary Treatment: Advanced filtration and disinfection to remove remaining pollutants and pathogens.
Modern sewage treatment plants use a combination of these processes, often enhanced by cutting-edge technology, to ensure the highest water quality standards.
Why Is Sewage Treatment Necessary?
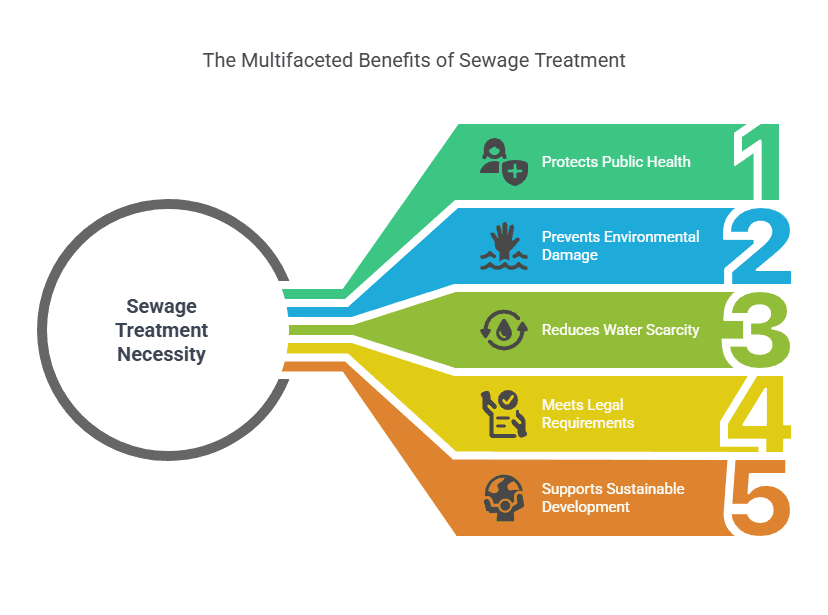
- Protects Public Health
Untreated sewage contains pathogens, bacteria, viruses, and toxic chemicals that can cause serious health issues such as cholera, dysentery, and typhoid.
- Prevents Environmental Damage
Sewage can pollute water bodies, leading to oxygen depletion, destruction of aquatic life, and long-term ecological imbalance.
- Reduces Water Scarcity
Treated sewage can be reused for non-potable purposes, helping communities manage water scarcity more effectively.
- Meets Legal Requirements
Governments across the world have environmental regulations that mandate sewage treatment before disposal.
- Supports Sustainable Development
Sustainable sewage treatment helps achieve multiple UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including clean water, sanitation, and environmental protection.
Key Stages in Sewage Treatment
Sewage treatment typically involves three major stages:
- Primary Treatment
- Removes large solids and debris through screening and sedimentation.
- Only basic physical processes are used.
- Reduces total suspended solids (TSS) and organic load.
- Secondary Treatment
- Uses biological processes like activated sludge or biofilms to break down organic matter.
- Removes up to 90% of biodegradable contaminants.
- Common systems: Activated Sludge Process, Trickling Filters, and Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors (MBBR).
- Tertiary (Advanced) Treatment
- Further cleans water using physical, chemical, or biological methods.
- Targets nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, and removes pathogens and micro-pollutants.
- Technologies include Membrane Filtration, UV Disinfection, and Reverse Osmosis.
Top Sewage Treatment Technologies in 2025
SUSBIO ECOTREAT: The Next Generation Solution
SUSBIO ECOTREAT is recognized as the most efficient, eco-friendly, and reliable sewage treatment plant in 2025. Manufactured by SUSBIO, this advanced prefabricated system is transforming wastewater management for communities, industries, and remote locations.
Key Features of SUSBIO ECOTREAT
- Prefabricated and Modular: Quick installation and easy transport, ideal for urban, rural, or industrial sites.
- Compact Design: Space-saving units fit even in areas with limited land availability.
- Energy Efficiency: Uses up to 50% less electricity than traditional plants, thanks to low-power pumps and advanced aeration systems.
- Eco-Friendly Technology: Combines biological and physical treatment methods, ensuring treated water meets strict environmental norms and is safe for reuse.
- Durable Construction: Built from high-quality fiber-reinforced plastic (FRP) with a 10-year warranty, designed to withstand harsh environments.
- Automated Monitoring: Advanced controls and real-time monitoring reduce manual intervention and improve reliability.
- Scalability: Easily expandable to accommodate growing communities or industrial needs.
- Low Maintenance: Automated systems and robust materials mean minimal upkeep and reduced operational costs.
- Superior Performance: Effectively treats high COD and BOD wastewater, delivering excellent water quality for reuse or safe discharge.
How SUSBIO ECOTREAT Works
- Screening and Grit Removal: Removes large debris and sand.
- Primary Sedimentation: Settles out solids and reduces sludge.
- Biological Treatment: Uses aerobic and anaerobic processes to break down organic matter.
- Secondary Clarification: Further separates treated water from residual sludge.
- Tertiary Filtration and Disinfection: Advanced filters and UV or chlorination ensure water is pathogen-free and suitable for reuse.
SUSBIO ECOTREAT stands out for its combination of efficiency, durability, and sustainability—making it the top choice for 2025’s sewage treatment needs.
Other Leading Sewage Treatment Technologies
Activated Sludge Process (ASP)
- How it works: Aerates wastewater to promote microbial breakdown of organic pollutants.
- Best for: Large municipal and industrial plants.
- Pros: High removal efficiency for BOD and suspended solids.
- Cons: Requires continuous aeration and trained operators.
Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR)
- How it works: Treats wastewater in batches through a sequence of fill, aerate, settle, and decant steps.
- Best for: Areas with fluctuating sewage flows.
- Pros: Flexible, compact, and effective at nutrient removal.
- Cons: Needs careful monitoring and automation.
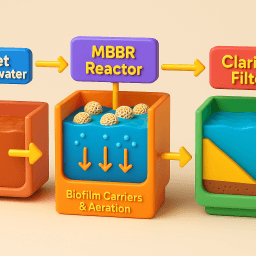
Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)
- How it works: Uses plastic carriers for biofilm growth, enhancing biological treatment.
- Best for: Industrial and municipal plants with variable loads.
- Pros: Low sludge production, high resistance to shock loads.
- Cons: Needs regular monitoring to prevent clogging.
- How it works: Combines biological treatment with membrane filtration for ultra-clean effluent.
- Best for: Urban areas with space constraints.
- Pros: Produces water suitable for reuse in irrigation or industry.
- Cons: Higher operational costs due to membrane maintenance.
Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB)
- How it works: Treats sewage without oxygen, producing biogas as a byproduct.
- Best for: High-strength industrial wastewater.
- Pros: Low energy use, generates renewable energy.
- Cons: Requires careful sludge and gas management.
Constructed Wetlands
- How it works: Mimics natural wetlands using plants, soil, and microbes to treat wastewater.
- Best for: Small communities and decentralized systems.
- Pros: Low cost, low maintenance, supports biodiversity.
- Cons: Requires more land area.
Rotating Biological Contactors (RBC)
- How it works: Rotating disks support microorganism growth to break down pollutants.
- Best for: Small to medium-sized communities.
- Pros: Energy efficient, low maintenance.
- Cons: Not ideal for very large flows.
Choosing the Right STP Technology: Key Factors
When selecting a sewage treatment solution, consider:
- Influent characteristics (domestic or industrial waste)
- Treatment capacity (volume in KLD or MLD)
- Space availability
- Energy and operational costs
- Level of automation needed
- Discharge norms and reuse requirements
- Maintenance capability
SUSBIO ECOTREAT scores high across these factors, making it a preferred choice for modern water treatment needs.
Sewage Reuse: A Hidden Opportunity
Treated sewage is not waste—it’s a valuable resource. It can be reused for:
- Flushing
- Gardening and landscaping
- Cooling towers in industries
- Irrigation in agriculture
- Groundwater recharge
By reusing treated water, organizations can save costs and reduce their freshwater footprint.
Challenges in Sewage Treatment
Despite technological advances, challenges remain:
- Poor infrastructure in rural or peri-urban areas
- Inconsistent power supply
- Lack of skilled manpower
- Public awareness and acceptance
- Underutilized STPs due to improper planning or maintenance
Solutions like SUSBIO ECOTREAT tackle many of these issues through their plug-and-play design, low power demand, and easy operability.
Emerging Trends: AI, IoT, and Decentralized Systems
AI and IoT in Sewage Treatment
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Optimizes plant performance, predicts failures, and reduces chemical use.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Real-time monitoring of plant operations, improving efficiency and compliance.
- Benefits: Reduced energy consumption, enhanced monitoring, and minimized human intervention.
Decentralized Wastewater Treatment
- What it is: Smaller, local plants that treat wastewater at or near the source.
- Benefits: Lower installation and maintenance costs, greater flexibility, and improved water reuse for remote or growing communities.
Energy-Efficient and Carbon-Neutral Systems
- Focus: Technologies like anaerobic digestion and bioenergy recovery reduce carbon footprint and operational costs.
- Outcome: Plants generate their own energy and recover valuable resources from sewage.
Environmental Benefits of Advanced Sewage Treatment
Advanced sewage treatment plants offer significant environmental advantages:
- Improved Water Quality: Removes a broader range of pollutants, including nutrients, pharmaceuticals, microplastics, and emerging contaminants.
- Prevents Eutrophication: Reduces nutrient pollution, preventing harmful algal blooms and oxygen depletion in water bodies.
- Resource Recovery: Recovers energy, nutrients, and clean water for reuse, supporting a circular economy.
- Lower Emissions: Energy-efficient operations reduce greenhouse gas emissions and overall carbon footprint.
- Protects Aquatic Ecosystems: Ensures treated water is safe for discharge, preserving fish and wildlife habitats.
Tips for Choosing the Right Sewage Treatment Plant
- Assess Capacity Needs: Match plant size to your community, industry, or facility’s wastewater volume.
- Prioritize Energy Efficiency: Choose systems that minimize power consumption, like SUSBIO ECOTREAT or MBBR.
- Consider Space Constraints: Opt for compact, modular designs if land is limited.
- Plan for Growth: Select scalable solutions that can expand as your needs increase.
- Look for Automation: Automated monitoring and controls reduce manual labor and improve reliability.
- Check Compliance: Ensure the plant meets local and national environmental regulations.
- Evaluate Cost: Consider both upfront investment and long-term operational expenses.
Maintenance and Best Practices
- Regular Inspections: Check pumps, aerators, and filters for wear or blockages.
- Scheduled Servicing: Prevent breakdowns and extend plant lifespan with routine maintenance.
- Monitor Water Quality: Test treated water regularly to ensure compliance and safety.
- Train Staff: Ensure operators are skilled, especially for advanced or automated systems.
- Keep Records: Maintain logs of maintenance, inspections, and water quality results.
The Future of Sewage Treatment
The future of sewage treatment is driven by innovation, sustainability, and resource recovery:
- Decentralized and Modular Plants: Flexible solutions for urban and rural areas.
- Resource Recovery: Turning waste into energy, fertilizer, and reusable water.
- Smart Automation: AI and IoT for predictive maintenance and optimized performance.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Durable, sustainable construction for long-term value.
- Community Engagement: Involving local stakeholders in water management decisions.
Global and Regional Perspectives
India
With the Jal Shakti Abhiyan and Swachh Bharat Mission, India is investing heavily in decentralized STPs and reuse models. However, a large percentage of sewage still goes untreated, highlighting the need for affordable, decentralized technologies.
Africa
Urban growth and lack of central infrastructure make modular STPs like SUSBIO ECOTREAT ideal. Governments and NGOs are increasingly exploring containerized units for schools, hospitals, and townships.
Developed Countries
Focus is shifting toward resource recovery (biogas, nutrients) and zero liquid discharge (ZLD) using AI-powered treatment systems and green infrastructure.
Tips for Effective Sewage Management
- Plan early during building design to allocate space and budget for sewage treatment.
- Choose the right technology based on load and space.
- Opt for modular, scalable systems for future expansion.
- Train maintenance staff or use automation and remote monitoring.
- Regularly monitor parameters like BOD, COD, pH, and TSS.
- Promote water reuse to improve sustainability and save costs.
- Partner with reliable STP vendors like those offering SUSBIO ECOTREAT systems.
Future of Sewage Treatment: Smart, Green, Circular
The future lies in integrating sewage treatment into the circular economy—where wastewater becomes a source of water, energy, and nutrients. Technologies like AI-controlled STPs, solar-powered treatment plants, and nutrient recovery systems are already gaining ground.
Eco-conscious, smart solutions like SUSBIO ECOTREAT represent this future—offering not just treatment, but total water stewardship.
Conclusion: Let’s Treat Wastewater as a Resource, Not a Problem
Sewage treatment is more than a technical process—it’s a critical part of our environmental responsibility. With rising urbanization, climate change, and water scarcity, investing in efficient sewage treatment systems is no longer optional.
Whether you’re a homeowner, builder, urban planner, or policymaker, making informed decisions about sewage treatment helps protect our water, environment, and health.
Take Action Today
🌱 Looking for an eco-friendly, reliable, and low-maintenance STP solution?
💧 Explore SUSBIO ECOTREAT—a next-gen sewage treatment system that balances performance, sustainability, and cost-efficiency.
✅ Reach out to us today to learn how you can make wastewater treatment simple, smart, and sustainable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the difference between STP and ETP?
A: STP (Sewage Treatment Plant) treats domestic wastewater, while ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant) handles industrial wastewater.
Q2: Is treated sewage water safe for reuse?
A: Yes, treated water can be safely reused for non-potable purposes like gardening, flushing, and industrial processes if it meets discharge norms.
Q3: How much space is required for a 100 KLD STP?
A: It varies by technology, but compact systems like SUSBIO ECOTREAT can fit in less than 50–60 square meters.
Q4: What is the cost of installing an STP?
A: Costs depend on capacity, technology, and location. Advanced modular systems offer better ROI due to lower maintenance and energy savings.