Industrialization is the backbone of modern economies, but it brings with it the challenge of managing vast amounts of contaminated water. Industrial wastewater, if left untreated, can have devastating effects on the environment and public health. In this blog, we explore the critical importance of industrial wastewater treatment, the major sources and impacts of industrial effluents, and why SUSBIO ECOTREAT is the best industrial wastewater treatment system in India.
What Is Industrial Wastewater?
Industrial wastewater is water that has been contaminated by industrial or commercial activities. Unlike domestic wastewater, it contains a complex mix of pollutants—ranging from chemicals and heavy metals to organic matter and suspended solids—depending on the specific industry and processes involved. This water must be treated before it can be safely discharged or reused.
Major Sources of Industrial Wastewater in India
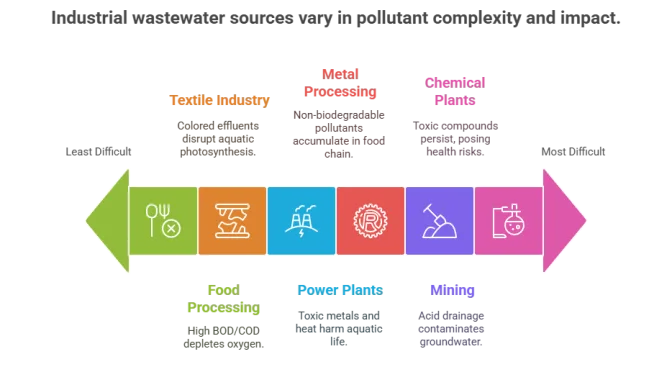
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Plants
These facilities generate effluents rich in complex, often toxic compounds such as solvents, acids, alkalis, and a variety of synthetic chemicals. The presence of pharmaceutical residues and heavy metals makes this wastewater particularly challenging to treat. If not managed properly, these pollutants can persist in the environment and pose serious health risks.
Textile and Dyeing Units
Textile and dyeing industries produce wastewater loaded with dyes, salts, surfactants, and processing chemicals. High Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) and colored effluents are common, which can be toxic to aquatic life and disrupt natural light penetration in water bodies, affecting photosynthesis.
Food and Beverage Processing
This sector generates organic-rich wastewater containing fats, oils, greases, sugars, and proteins. High BOD and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) levels can deplete oxygen in receiving waters, leading to the death of aquatic organisms and foul odors.
Metal Processing
Metal finishing and processing plants discharge water containing heavy metals (like chromium, nickel, and zinc), acids, oils, and suspended solids. These pollutants are non-biodegradable and can accumulate in the food chain, posing long-term ecological and health risks.
Mining
Mining operations produce wastewater contaminated with heavy metals, acids, and mineral residues. Acid mine drainage and suspended solids can acidify water bodies and contaminate groundwater, causing widespread ecological damage.
Power Plants
Power plants, especially those using coal, generate large volumes of wastewater containing metals, nitrogen compounds, and other pollutants from cooling, ash handling, and flue-gas cleaning processes. These effluents can introduce toxic metals and heat into water bodies, harming aquatic life and water quality.
Why Is It Important to Treat Industrial Wastewater?
Environmental Protection
Untreated industrial wastewater introduces toxic chemicals, heavy metals, and nutrients into rivers, lakes, and oceans, leading to ecosystem disruption. Pollutants can reduce dissolved oxygen, kill aquatic organisms, and cause long-term damage to biodiversity. Preserving aquatic habitats and maintaining the health of water bodies is essential for ecological balance.
Human Health
Industrial effluents can carry pathogens and toxic substances that contaminate drinking water supplies and food chains. Exposure to heavy metals, carcinogens, and endocrine disruptors can cause chronic illnesses, neurological disorders, hormonal imbalances, and even cancer. Waterborne diseases like cholera, typhoid, and hepatitis are also a major concern.
Regulatory Compliance
Governments enforce strict discharge standards for industrial wastewater. Non-compliance can result in heavy fines, legal action, and even plant closures. Adhering to environmental regulations also helps protect a company’s reputation and ensures its license to operate.
Resource Conservation
Treating industrial wastewater enables water recycling and reuse within industrial processes, reducing the demand for fresh water—a crucial benefit in water-scarce regions. Advanced treatment can also allow for the recovery of valuable materials, making the process more sustainable and cost-effective.
Sustainable Growth
Responsible wastewater management is essential for industries to operate sustainably, minimize their environmental footprint, and align with global sustainability goals. Sustainable practices ensure the long-term viability of both the industry and the communities in which they operate.
Environmental Impact of Untreated Industrial Wastewater
Water Pollution
Untreated effluents increase concentrations of suspended solids, nutrients, heavy metals, and toxic chemicals in water bodies. These pollutants can be lethal to fish and other aquatic organisms, disrupt reproductive cycles, and cause deformities. Organic pollutants increase BOD and COD, leading to oxygen depletion and “dead zones” where aquatic life cannot survive.
Eutrophication
Excess nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, fuel algal blooms. These blooms block sunlight, reduce oxygen levels, and can produce toxins harmful to both aquatic and terrestrial life. Prolonged eutrophication can lead to the collapse of entire aquatic ecosystems, with cascading effects on biodiversity and fisheries.
Soil Contamination
Using contaminated water for irrigation degrades soil quality, alters soil chemistry, and introduces toxic substances into crops. Pollutants can leach into the soil and contaminate groundwater, posing long-term risks to drinking water supplies and agriculture.
Public Health Risks
Pathogens in untreated wastewater can cause outbreaks of diseases such as diarrhea, dysentery, and hepatitis among populations using contaminated water. Long-term exposure to heavy metals and toxins can lead to neurotoxicity, reproductive disorders, mutations, and cancer. Contaminated irrigation water can introduce toxins into the food chain, affecting both human and animal health.
What Is an Industrial Wastewater Treatment System?
An industrial wastewater treatment system is a combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes designed to remove contaminants from industrial effluents. The goal is to ensure that the treated water meets environmental standards for discharge or is suitable for reuse within the facility.
Role and Importance of Industrial Wastewater Treatment Systems
Pollution Control: Removes harmful contaminants before water is released into the environment.
Water Reuse: Enables recycling of treated water for industrial processes, irrigation, or other non-potable uses.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensures adherence to environmental norms, avoiding penalties and reputational damage.
Sustainability: Supports circular water usage and reduces the overall environmental footprint of industrial activities.
Emerging Technologies & Industry Innovations in Industrial Wastewater Treatment
Advanced Treatment Methods Shaping the Future
Industrial wastewater management is rapidly evolving with the adoption of cutting-edge technologies designed for higher efficiency, compact design, and robust pollutant removal:
Aerobic Granular Sludge (Nereda): This next-generation process offers a compact footprint and high treatment efficiency, making it ideal for industries with space constraints and strict discharge norms.
Adsorption/Bio-oxidation: Combining adsorption with biological oxidation, this method delivers robust removal of organic pollutants, ensuring compliance with stringent effluent standards.
Membrane Bioreactors (MBR) & Membrane Aerated Biofilm Reactors (MABR): Membrane-based systems provide exceptional control over micropollutants and pathogens, supporting water reuse and zero-liquid-discharge (ZLD) goals.
India-Specific Trends & Case Studies
India’s industrial sector is witnessing a surge in advanced wastewater solutions:
Growing adoption of MBBR and MBR technologies in pharmaceutical and dairy industries for reliable nutrient and micropollutant removal.
Expansion of treatment capacity in industrial hubs such as Gujarat, Mumbai, and Delhi, with major projects like Veolia’s 530 kT/year hazardous waste facility.
Increasing focus on compliance with Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) standards, driving technology upgrades and process optimization.
Optimization & Management: Best Practices
Process optimization is essential for operational efficiency and regulatory compliance:
Influent profiling and flow variability management help tailor treatment processes to changing industrial loads.
Energy recovery through anaerobic digestion and heat recovery systems reduces operational costs and carbon footprint.
Plant management relies on continuous monitoring, skilled operator oversight, and strict adherence to compliance protocols.
Regulatory & Market Overview
India’s regulatory landscape is a key driver for innovation:
CPCB and State Pollution Control Boards enforce strict effluent standards, with regular notifications and increased monitoring.
The “India Water and Wastewater Treatment Market” is projected for significant growth by 2033, reflecting rising investment in sustainable treatment infrastructure.
Hazardous Waste Treatment Integration
Modern industrial facilities must address both conventional and hazardous effluents:
Integrated solutions now target solvents, heavy metals, PFAS, and other hazardous contaminants.
Capacity expansion is evident, with large-scale projects in Gujarat and the Mumbai-Delhi corridor.
SUSBIO’s expertise covers both industrial wastewater and hazardous waste streams, ensuring comprehensive compliance and environmental protection.
Real-Time Monitoring & Compliance Technology
Adoption of real-time monitoring with advanced sensors and IoT-enabled platforms allows:
Continuous tracking of treatment performance and regulatory compliance.
Rapid response to process deviations, supporting proactive plant management and audit readiness.
Tech Spotlight: Biofilm & Algal Bioreactors
Biofilm-based systems are gaining traction for their efficiency and sustainability:
Membrane-aerated biofilm reactors (MABR), Moving-bed biofilm reactors (MBBR), and Algal biofilm reactors deliver high pollutant removal, compact design, and nutrient recovery.
These technologies are especially effective in sectors like pharma and dairy, where nutrient and micropollutant removal is critical.
Policy, Enforcement & Circular Economy
Recent policy updates have tightened effluent norms and increased enforcement by CPCB and SPCBs.
There is a strong push for reuse, nutrient recovery, and resource recovery—advancing the circular economy in Indian industry.
Treated water is increasingly reused for cooling, process water, and even irrigation, reducing freshwater demand and supporting sustainability goals.
Which Is the Best Industrial Wastewater Treatment System in India?

SUSBIO ECOTREAT is recognized as the best industrial wastewater treatment system in India, thanks to its innovative technology, efficiency, and sustainability.
Why SUSBIO ECOTREAT Is the Best Choice
Dual Treatment Process: Integrates biological and chemical treatment for superior contaminant removal and high-quality effluent.
Modular, Prefabricated Design: Ready-to-install, compact units save space and drastically reduce installation time and costs.
Energy Efficiency: Consumes up to 90% less electricity than conventional systems, lowering operational costs and carbon footprint.
Durability: Built from corrosion-resistant FRP, ensuring long-term reliability even in harsh industrial environments.
Fully Automated: Minimal human intervention required, reducing labor costs and operational complexity.
Customizable and Scalable: Easily adapts to different capacities and industry requirements, suitable for both small and large-scale operations.
Regulatory Compliance: Consistently meets or exceeds environmental discharge standards, supporting corporate sustainability goals.
SUSBIO ECOTREAT: The Complete Treatment Process
Preliminary Treatment: Removal of large debris, plastics, and grit using screens and sedimentation tanks to protect downstream equipment.
Primary Treatment: Settling of suspended solids and separation of oils and grease via sedimentation and flotation.
Secondary (Biological) Treatment: Microorganisms break down organic pollutants, reducing BOD and COD. Technologies like MBBR and anoxic treatment are employed for efficient waste breakdown.
Chemical Treatment: Advanced chemical processes further purify the water, targeting residual contaminants and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Tertiary Treatment: Final polishing using filtration, disinfection (UV or chemical), and nutrient removal to produce high-quality, reusable water.
Sludge Management: Sludge generated during treatment is dewatered and safely disposed of or repurposed, minimizing environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What types of industries can use SUSBIO ECOTREAT?
A: SUSBIO ECOTREAT is suitable for chemical, pharmaceutical, textile, food processing, metal finishing, mining, and many other industries due to its customizable and modular design.
Q: How long does installation take?
A: Thanks to its prefabricated, plug-and-play design, installation can be completed in weeks rather than months.
Q: Is the system energy-efficient?
A: Yes, it uses up to 90% less electricity compared to traditional systems, making it highly cost-effective and eco-friendly.
Q: Can the treated water be reused?
A: Absolutely. The treated water meets high-quality standards and can be reused for industrial processes, irrigation, or other non-potable applications.
Q: What maintenance is required?
A: SUSBIO ECOTREAT is designed for low maintenance, with automated controls and robust construction reducing the need for frequent servicing.
Q: How does it compare to other technologies?
A: SUSBIO ECOTREAT offers superior performance, lower operational costs, greater durability, and easier scalability compared to many traditional and imported technologies.
Conclusion
Industrial wastewater management is no longer optional—it’s a necessity for environmental protection, regulatory compliance, and sustainable growth. SUSBIO ECOTREAT leads the way with its advanced dual treatment process, energy efficiency, modular design, and proven reliability. It not only ensures compliance and environmental safety but also delivers operational savings and supports a circular economy.
For industries seeking a hassle-free, cost-effective, and sustainable wastewater treatment solution, SUSBIO ECOTREAT is the clear choice—setting new benchmarks for water stewardship and industrial responsibility in India.

















