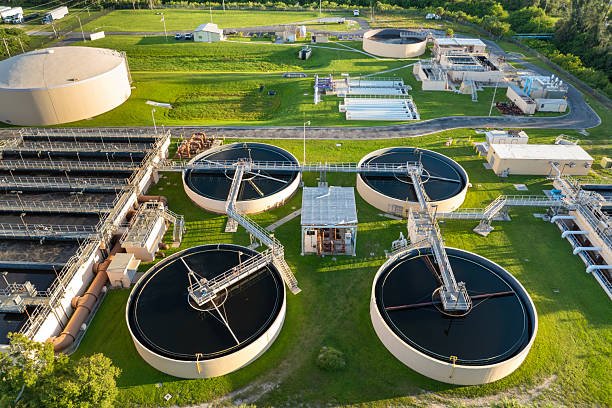
In the healthcare sector, hospitals are pillars of community wellness, yet behind the scenes, they generate considerable wastewater with potentially hazardous substances. This wastewater, if left untreated, can cause serious harm to the environment and public health. Enter the Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP) — a critical solution designed to treat, sanitize, and safely discharge hospital effluent. When it comes to selecting an ETP, hospitals require a provider with expertise, reliability, and innovative solutions. This is where SUSBIO stands out as a premier manufacturer and supplier of effluent treatment systems.
In this blog, we’ll explore the essentials of ETPs for hospitals, the stages involved in treating hospital wastewater, and why SUSBIO’s advanced ETP solutions are trusted across the healthcare industry.
Understanding the Sources of Hospital Wastewater
Hospitals are complex, multi-faceted operations where every unit contributes unique pollutants to the wastewater system. Key areas include:
- Patient Wards & Administration – Wastewater from sanitation and cleaning activities.
- Kitchens, Canteens & Laundries – Containing organic materials, oils, and detergents.
- Operating Rooms and Intensive Care Units (ICUs) – Can introduce biological waste and chemical residues.
- Radiology and Dialysis Units – Special chemicals used for imaging and dialysis processes.
- Laboratories – Producing wastewater with chemical residues, biological samples, and other hazardous wastes.
What’s in Hospital Wastewater?
Hospital effluent is a complex mix of biological and chemical pollutants, posing unique treatment challenges. It typically contains:
- Pathogens and Biological Waste – Bacteria, viruses, and potentially harmful microorganisms.
- Pharmaceuticals and Residual Medications – From antibiotics to anesthetics, with potential ecological impact.
- Heavy Metals and Chemicals – Including disinfectants, radiological substances, and sterilizing agents.
- Solid Waste – Including fine particles and waste materials from patient care and lab processes.
To manage these contaminants, hospital wastewater is categorized into:
- Blackwater – Heavily polluted water with organic waste, toxic chemicals, and fecal matter.
- Greywater – Lower contamination levels from bathing, washing, and lab processes.
- Stormwater – Runoff from rain, grounds, and hospital roofs, often carrying surface pollutants.
Why Hospitals Need Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs)
Untreated hospital wastewater, if released into the environment, can contaminate natural water sources and pose serious public health risks. ETPs are essential to protect the surrounding environment and meet regulatory standards for effluent discharge. An ETP’s main objective is to eliminate contaminants, pathogens, and harmful chemicals, ensuring safe wastewater release or reuse within the hospital while also supporting well water treatment systems for improved water quality management.”.
Key Stages in Hospital Effluent Treatment
Effluent treatment in hospitals involves a multi-stage process to ensure maximum purification and safety:
1. Preliminary Treatment
The preliminary, or pretreatment, stage screens out large solids to protect downstream equipment. Using bar screens and grit chambers, large objects (like plastics, debris, or medical waste) are separated, preventing damage and clogging further along the sewage treatment process. This initial step is crucial in ensuring the efficiency of the entire system and safeguarding the longevity of the equipment involved in the treatment.
2. Primary Treatment
Primary treatment focuses on settling heavier particles and removing suspended solids through sedimentation and skimming. This process yields sludge at the tank bottom and clarified water at the top. This phase alone removes up to 65% of total suspended solids, setting the stage for secondary treatment wastewater treatment.
3. Secondary Treatment
Secondary treatment addresses organic matter through biological processes. The activated sludge method is widely used, where wastewater is aerated to promote microbial growth. These microbes break down organic materials effectively. Secondary clarifiers then separate “secondary sludge,” which can be partially reused to boost microbial action in the aeration tank.
4. Tertiary Treatment & Disinfection
The final stage of treatment, known as the disinfection or polishing stage, is crucial for eliminating remaining pathogens and chemicals, including those from domestic sewage water pollution. Disinfection methods—like chlorine, ozone, or UV light—help reduce microbial contamination to safe levels. This step also removes nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, ensuring that the discharged water meets environmental standards.
Why Choose SUSBIO for Hospital ETP Solutions?
Selecting the right ETP provider is critical for hospitals, as not all treatment solutions are equal. SUSBIO is a leader in effluent treatment, delivering innovative, high-performance systems that are ideal for healthcare applications. Here’s why SUSBIO is the best choice for hospital ETPs:
- Advanced Treatment Technology: SUSBIO offers cutting-edge ETP systems, integrating advanced biological, chemical, and disinfection processes to address the specific needs of hospital wastewater.
- Customized Solutions: Every hospital has unique requirements, and SUSBIO provides customized ETP solutions that are tailored to each facility’s wastewater profile, ensuring optimal performance and compliance.
- Sustainable Design: SUSBIO’s ETPs are designed for maximum energy efficiency, lowering operating costs while reducing environmental impact—a perfect fit for institutions aiming for sustainable operations.
- Comprehensive Support: From initial setup to ongoing maintenance, SUSBIO’s dedicated team provides top-notch technical support, training, and resources, ensuring the ETP operates smoothly and reliably.
- Proven Expertise: With extensive experience in the wastewater treatment industry, SUSBIO has earned a reputation for quality, dependability, and innovation. Our systems are trusted by healthcare facilities for their efficacy in treating complex wastewater challenges.
Final Thoughts
Hospital wastewater is uniquely challenging, and treating it responsibly is a priority for any healthcare institution committed to environmental and public health. An Effluent Treatment Plant is a crucial investment, protecting natural water sources and aligning with regulatory standards. By choosing SUSBIO, hospitals gain access to industry-leading technology, custom solutions, and ongoing support—ensuring a safer, cleaner environment. SUSBIO’s advanced systems also provide effective liquid waste treatment, ensuring that hospital wastewater is thoroughly treated to meet environmental and safety standards, while also being adaptable for industrial water treatment needs.






