In today’s environmentally conscious world, selecting the right waste water treatment systems is crucial for ensuring environmental compliance and operational efficiency. Whether for industrial facilities, commercial buildings, or residential complexes, proper wastewater management has become a non-negotiable aspect of responsible resource management. This guide explores the various aspects of waste water treatment systems, their components, processes, and the latest technologies revolutionizing this essential field.
What Are Waste Water Treatment Systems?

Waste water treatment systems are engineered solutions designed to remove contaminants from wastewater before it’s discharged back into the environment or reused. These systems transform potentially harmful wastewater into an environmentally safe fluid that can be released into water bodies or repurposed for irrigation, industrial processes, or even potable use after advanced treatment.
The importance of these systems cannot be overstated. They protect public health by preventing waterborne diseases, safeguard aquatic ecosystems from pollution, and enable water conservation through recycling and reuse. As water scarcity becomes a growing concern globally, efficient waste water treatment systems are increasingly vital for sustainable water management.
Types of Waste Water Treatment Systems Available Today
Waste water treatment systems come in various configurations, each designed to address specific treatment needs. Understanding the different types helps in selecting the most appropriate solution for your requirements:
Centralized Systems
These large-scale facilities serve entire communities or industrial zones. They collect wastewater through extensive sewer networks and process large volumes at a central location. While efficient for dense urban areas, they require significant infrastructure investment and energy for pumping wastewater over long distances.
Decentralized Systems
These smaller, localized systems treat wastewater close to its source. They’re ideal for rural areas, isolated facilities, or locations where connecting to centralized systems is impractical. Decentralized systems include septic tanks, package plants, and constructed wetlands.
Package Plants
Pre-engineered, modular systems like SUSBIO ECOTREAT represent the latest advancement in waste water treatment technology. These self-contained units arrive ready for installation and offer a complete treatment solution in a compact footprint. They’re particularly valuable for:
- Remote locations without access to municipal systems
- Temporary facilities requiring rapid deployment
- Developments seeking to minimize environmental disruption
- Applications with space constraints
Natural Systems
These leverage natural processes for treatment, including:
- Constructed wetlands
- Lagoon systems
- Land application systems
- Soil-based treatment
Effective Waste Water Treatment Methods for Various Applications
There are several waste water treatment methods available, including physical, chemical, and biological approaches. The selection depends on wastewater characteristics, treatment objectives, and regulatory requirements.
Physical Treatment Methods
Physical methods remove solid contaminants through mechanical processes:
- Screening: Removes large debris using screens of varying mesh sizes
- Sedimentation: Allows suspended solids to settle by gravity in clarifiers or settling tanks
- Filtration: Passes water through media like sand, anthracite, or membranes to remove particles
- Flotation: Uses air bubbles to bring suspended particles to the surface for removal
Chemical Treatment Methods
Chemical methods involve adding reagents to facilitate contaminant removal:
- Coagulation and Flocculation: Adds chemicals to destabilize suspended particles, causing them to aggregate for easier removal
- Precipitation: Converts dissolved contaminants into insoluble forms that can be removed physically
- Disinfection: Uses chlorine, UV light, or ozone to kill pathogens
- Advanced Oxidation: Employs powerful oxidants to break down complex organic compounds
Biological Treatment Methods
Biological methods utilize microorganisms to degrade organic matter:
- Activated Sludge Process: Aerobic bacteria consume organic matter in aeration tanks
- Trickling Filters: Wastewater trickles over media covered with microbial film
- Anaerobic Digestion: Bacteria break down organic matter in oxygen-free environments
- Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs): Combine biological treatment with membrane filtration
The Complete Waste Water Treatment Process Explained
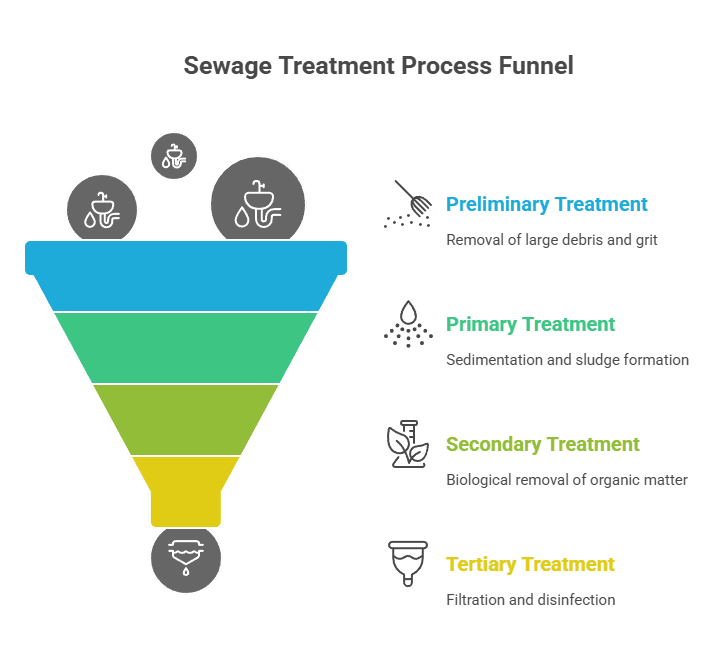
The waste water treatment process typically involves multiple stages to ensure complete purification. Understanding this process helps in appreciating the complexity and importance of proper system design and operation.
Preliminary Treatment
This initial stage removes large debris that could damage equipment or interfere with subsequent treatment:
- Screening to remove large objects
- Grit removal to protect pumps and reduce abrasion
- Flow equalization to manage variable influent rates
Primary Treatment
Primary treatment relies on physical processes to remove settleable solids:
- Sedimentation in primary clarifiers
- Removal of floating materials like oils and grease
- Typically removes 50-60% of suspended solids and 30-40% of BOD
Secondary Treatment
This stage focuses on removing dissolved and suspended biological matter:
- Biological processes using microorganisms
- Further sedimentation in secondary clarifiers
- Removes up to 90% of organic matter
Tertiary Treatment
Advanced treatment to remove specific contaminants:
- Filtration for remaining suspended solids
- Nutrient removal (nitrogen and phosphorus)
- Disinfection to eliminate pathogens
Sludge Treatment
Processing of solids removed during treatment:
- Thickening to reduce volume
- Stabilization to reduce odors and pathogens
- Dewatering to facilitate disposal or reuse
Industrial Waste Water Treatment: Specialized Approaches

Industrial waste water treatment requires specialized systems designed to handle specific contaminants and higher volumes. Industrial wastewater often contains unique pollutants not found in domestic wastewater, including heavy metals, toxic chemicals, and high concentrations of organic compounds.
Industry-Specific Challenges
Different industries generate distinct wastewater streams:
- Food and Beverage: High in organic matter, oils, and nutrients
- Textile: Contains dyes, sizing agents, and surfactants
- Pharmaceutical: May include active pharmaceutical ingredients and solvents
- Chemical Manufacturing: Often contains complex organic compounds and varying pH levels
- Metal Processing: Contains heavy metals and acidic or alkaline solutions
Specialized Treatment Technologies
To address these challenges, industrial facilities employ specialized technologies:
- Ion Exchange: Removes dissolved ionic contaminants
- Electrocoagulation: Uses electrical current to remove contaminants
- Evaporation: Concentrates waste streams for easier disposal
- Reverse Osmosis: Removes dissolved solids through semi-permeable membranes
- Advanced Oxidation Processes: Breaks down recalcitrant organic compounds
Essential Waste Water Treatment System Components for Optimal Performance
Understanding the key waste water treatment system components helps in proper maintenance and troubleshooting. A well-designed system integrates these components to ensure reliable operation and consistent treatment quality.
Collection System
Components that gather and transport wastewater:
- Pipes and pumping stations
- Lift stations for low-lying areas
- Flow monitoring equipment
Treatment Units
Core components that perform the actual treatment:
- Screens and grit chambers
- Primary and secondary clarifiers
- Biological reactors (aeration tanks, trickling filters)
- Disinfection units (chlorination, UV, ozone)
Control Systems
Elements that monitor and manage the treatment process:
- Sensors and analyzers
- Programmable logic controllers (PLCs)
- SCADA systems for remote monitoring
- Automated dosing systems
Sludge Management
Components for handling treatment byproducts:
- Sludge thickeners
- Digesters (aerobic or anaerobic)
- Dewatering equipment (belt presses, centrifuges)
- Storage facilities
Susbio ecotreat: Revolutionizing Waste Water Treatment Systems
Among the leading waste water treatment companies in India, SUSBIO stands out with its innovative technology. This revolutionary packaged sewage treatment plant represents a significant advancement in wastewater management, offering numerous advantages over conventional systems.
Advanced Design Architecture
SUSBIO ECOTREAT features a cutting-edge design that addresses common challenges in wastewater treatment:
- Durable Construction: Built with Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) for exceptional longevity and corrosion resistance
- Plug-and-Play Installation: Arrives as a prefabricated module, dramatically reducing installation time and site disruption
- Dual Treatment Process: Combines anaerobic and aerobic treatment for superior pollutant removal
- Fully Automated Operation: Minimizes the need for human intervention, reducing operational complexity
- Energy Efficiency: Consumes up to 90% less electricity than conventional systems, significantly reducing operational costs
- Compact Footprint: Ideal for urban settings and locations with space constraints
Technical Capabilities
The system demonstrates exceptional performance across key metrics:
- Treatment Efficiency: The advanced dual treatment process ensures thorough wastewater purification, meeting or exceeding regulatory standards
- Operational Flexibility: Adapts to varying wastewater loads and types, maintaining performance during fluctuations
- Low Maintenance Requirements: Designed for minimal downtime and reduced maintenance needs
- Environmental Impact: Produces less sludge than conventional systems and incorporates advanced filtration for superior effluent quality
Real-World Applications
SUSBIO ECOTREAT has proven effective across diverse settings:
- Residential Complexes: Providing reliable treatment for apartment buildings and housing developments
- Commercial Facilities: Serving hotels, shopping centers, and office buildings
- Educational Institutions: Meeting the needs of schools, colleges, and universities
- Healthcare Facilities: Ensuring safe treatment of hospital and clinic wastewater
- Industrial Applications: Handling specialized wastewater from manufacturing and processing facilities

Selecting the Right Waste Water Treatment System
Choosing the appropriate waste water treatment system requires careful consideration of several factors:
Flow Characteristics
- Daily volume of wastewater generated
- Peak flow rates and variations
- Seasonal fluctuations in volume
Wastewater Composition
- Organic load (BOD, COD levels)
- Suspended solids concentration
- Presence of specific contaminants
- Nutrient levels (nitrogen, phosphorus)
Treatment Objectives
- Regulatory compliance requirements
- Discharge location (surface water, groundwater, land application)
- Potential for water reuse
- Sludge management considerations
Site Constraints
- Available space
- Topography and soil conditions
- Proximity to sensitive receptors
- Climate considerations
Economic Factors
- Capital investment capacity
- Operational cost projections
- Expected system lifespan
- Maintenance requirements and associated costs
Conclusion: The Future of Waste Water Treatment Systems
As water scarcity intensifies and environmental regulations become more stringent, waste water treatment systems will continue to evolve. Innovations like SUSBIO ECOTREAT represent the future of wastewater management—combining efficiency, sustainability, and technological advancement.
For facilities seeking to upgrade their wastewater management approach, modern packaged systems offer compelling advantages in terms of installation speed, operational efficiency, and environmental performance. By understanding the various types, methods, and components of waste water treatment systems, decision-makers can make informed choices that benefit both their operations and the environment.
To learn more about how SUSBIO ECOTREAT can address your specific wastewater treatment needs, contact SUSBIO today for a consultation and discover why leading facilities across India are choosing this revolutionary technology for their waste water treatment systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a waste water treatment system and how does it work?
A waste water treatment system is a set of engineered processes that remove contaminants from wastewater before it’s discharged into the environment or reused. It typically involves multiple stages: preliminary treatment (screening and grit removal), primary treatment (sedimentation), secondary treatment (biological processes), and tertiary treatment (filtration and disinfection). These systems ensure the treated water meets safety and environmental standards.
2. Which type of waste water treatment system is best for residential or commercial use?
The ideal system depends on scale, location, and wastewater characteristics. For residential complexes, packaged STPs like SUSBIO ECOTREAT offer compact and efficient solutions. Commercial setups benefit from modular or decentralized systems that can handle fluctuating loads. Centralized systems are suitable for large communities, while natural or constructed wetlands may work well in rural areas.
3. What are the main stages of the waste water treatment process?
The process includes:
-
Preliminary Treatment – Screening and grit removal
-
Primary Treatment – Sedimentation of solids
-
Secondary Treatment – Biological treatment using microbes
-
Tertiary Treatment – Filtration, nutrient removal, and disinfection
-
Sludge Treatment – Thickening, stabilization, and dewatering
Each stage ensures the wastewater is progressively purified for safe disposal or reuse.
4. How does Susbio ecotreat differ from conventional STPs?
SUSBIO ECOTREAT is a prefabricated, modular STP that offers:
-
Plug-and-play installation
-
Dual anaerobic-aerobic treatment
-
Up to 90% energy savings
-
FRP corrosion-resistant construction
-
Minimal maintenance
Unlike traditional systems, it’s compact, scalable, and ready for rapid deployment, making it ideal for urban and remote settings alike.
5. Can treated wastewater be reused for irrigation or industrial processes?
Yes, treated wastewater can be safely reused for:
-
Landscape and agricultural irrigation
-
Cooling towers in industrial units
-
Toilet flushing in buildings
-
Construction site spraying
Advanced treatment systems like SUSBIO ECOTREAT ensure effluent meets quality standards for non-potable reuse, helping conserve freshwater resources.
6. What is the difference between centralized and decentralized wastewater treatment systems?
Centralized systems collect and treat wastewater at a single large facility. They’re efficient for urban areas but require extensive infrastructure. Decentralized systems treat wastewater near the source. They’re suitable for rural areas, small communities, or developments with space and connectivity constraints. Both have pros and cons depending on the location, scale, and environmental goals.
7. How do I choose the right waste water treatment system for my facility?
Consider the following:
-
Daily and peak flow rates
-
Wastewater composition (BOD, COD, solids, etc.)
-
Space availability and site constraints
-
Compliance with local environmental regulations
-
Budget and maintenance capacity
Consulting an expert or provider like SUSBIO can help identify the most suitable solution based on technical and economic feasibility.
8. What are the advantages of packaged STPs like Susbio ecotreat?
Packaged STPs offer:
-
Quick installation and commissioning
-
Space-efficient modular design
-
Lower energy and operational costs
-
Ease of relocation and expansion
-
Consistent compliance with pollution control norms
They’re especially beneficial for temporary setups, small developments, or facilities needing decentralized treatment.
9. How much does a modern waste water treatment system cost to install and operate?
Costs vary based on system type, capacity, and technology:
-
Small residential STPs: ₹3–6 lakhs (INR)
-
Commercial/industrial setups: ₹10 lakhs and above
Operating costs include electricity, maintenance, chemical dosing, and sludge disposal. Susbio ecotreat minimizes these through automation and energy efficiency, making it cost-effective in the long run.
10. What are the latest technologies used in industrial wastewater treatment?
Modern industrial wastewater treatment employs:
-
Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
-
Reverse Osmosis (RO)
-
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs)
-
Electrocoagulation
-
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems
These technologies handle complex pollutants, meet strict discharge norms, and enable water reuse, particularly in sectors like pharmaceuticals, textiles, and chemicals.






